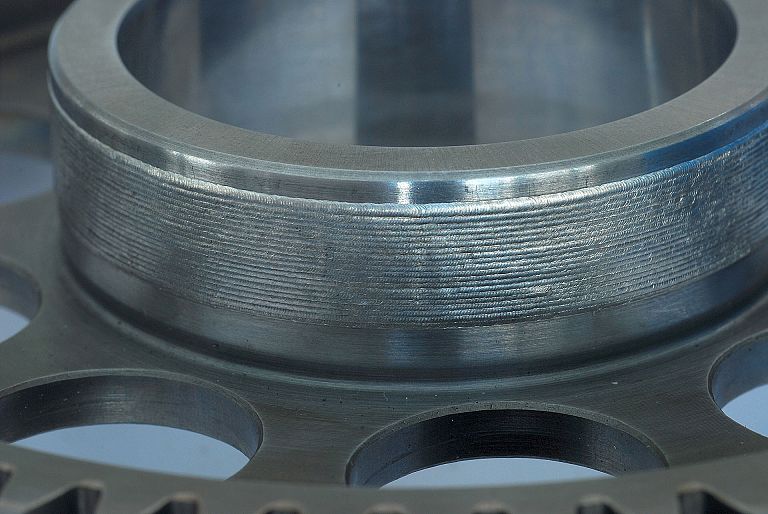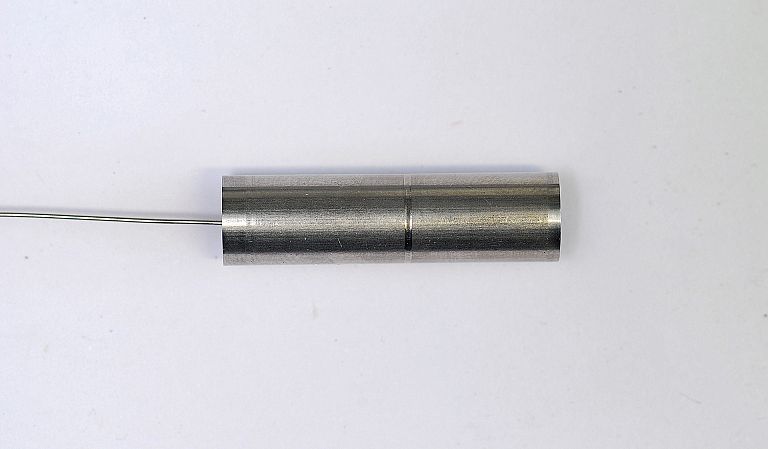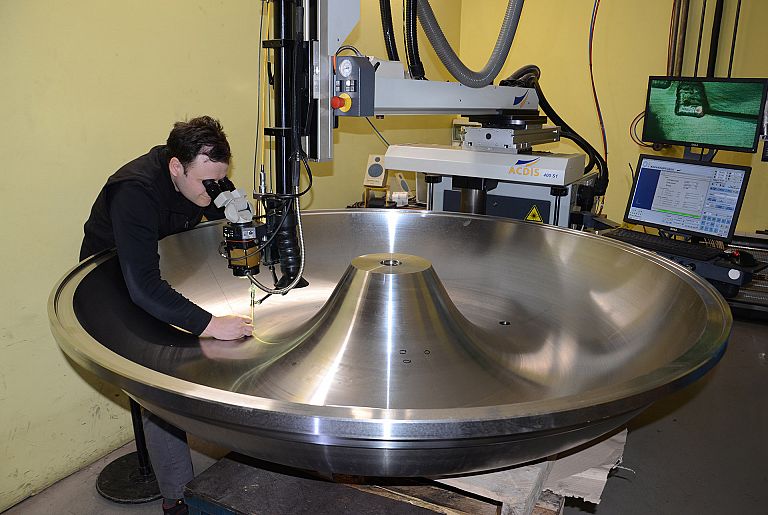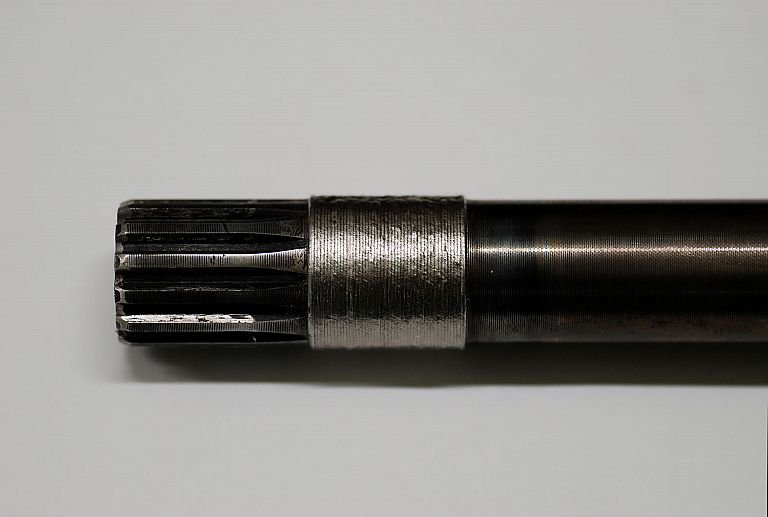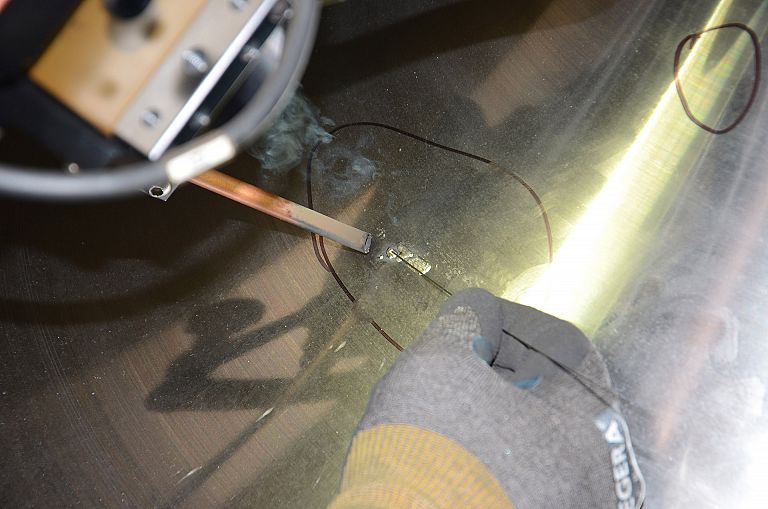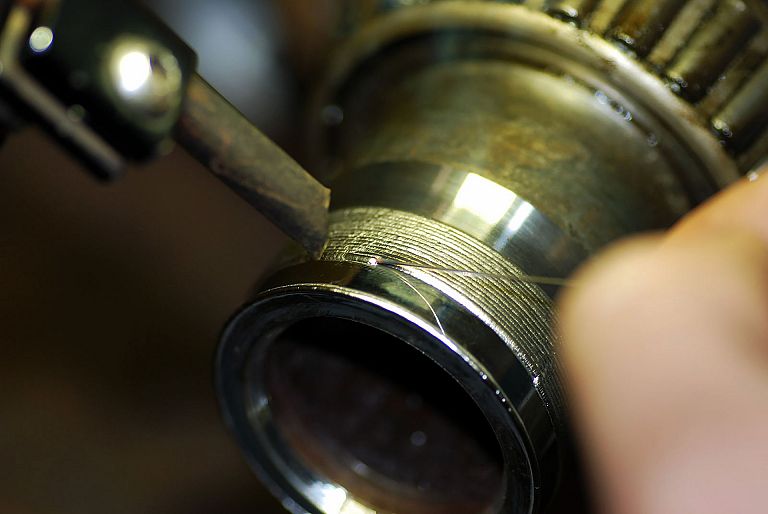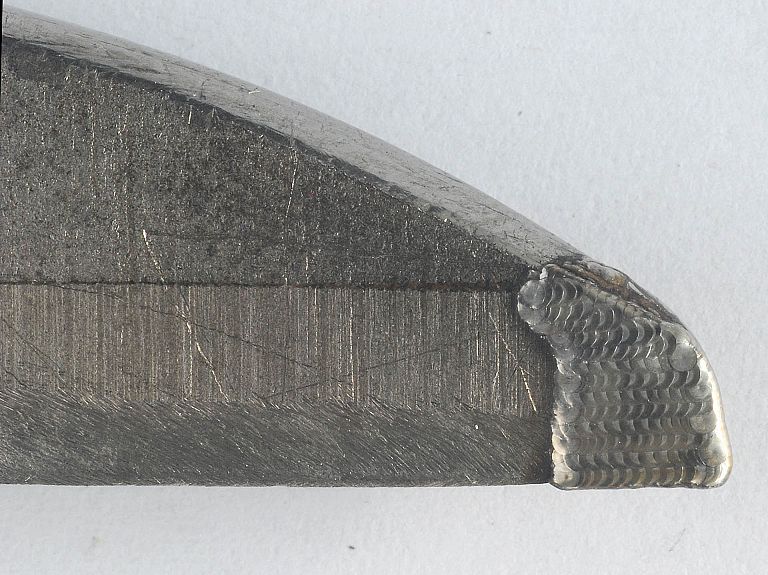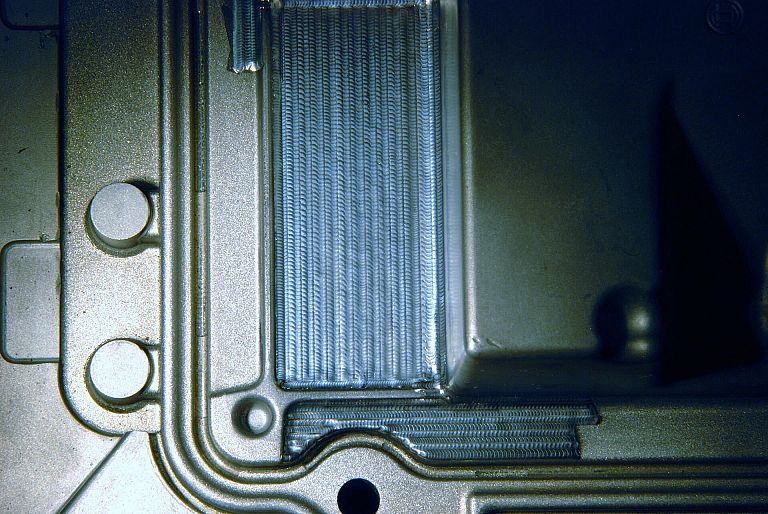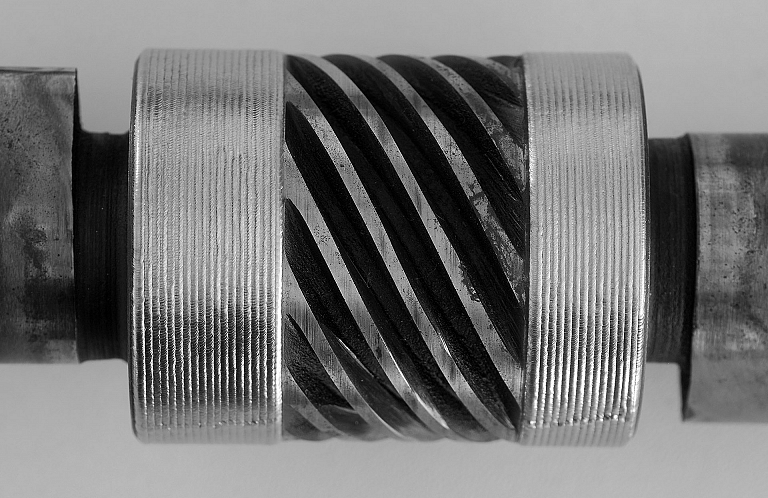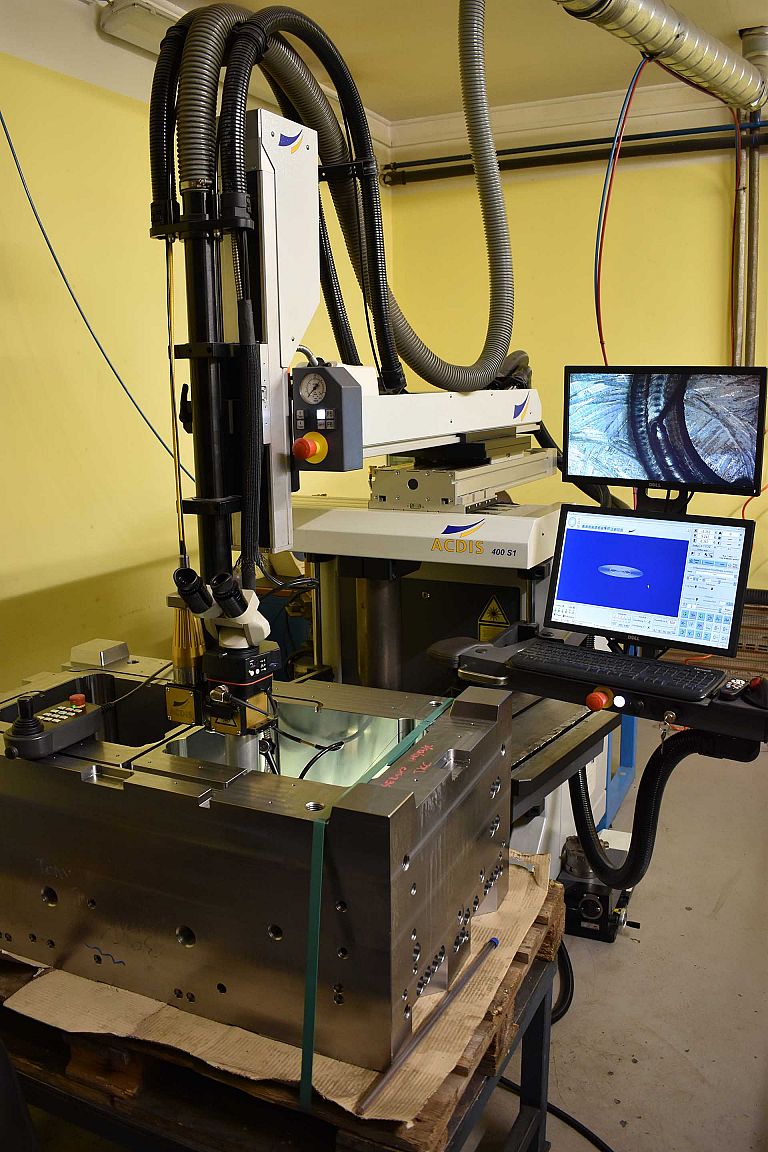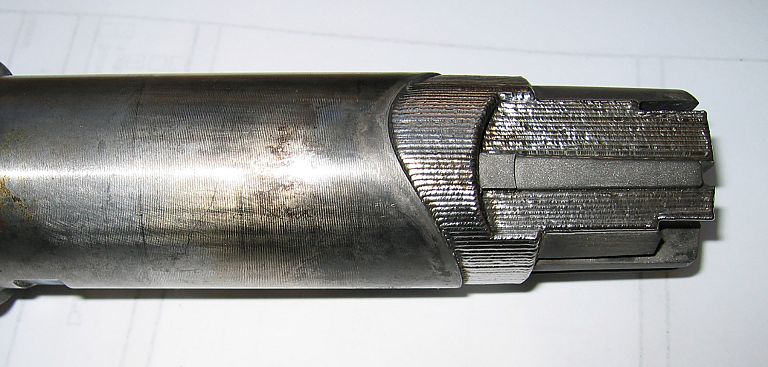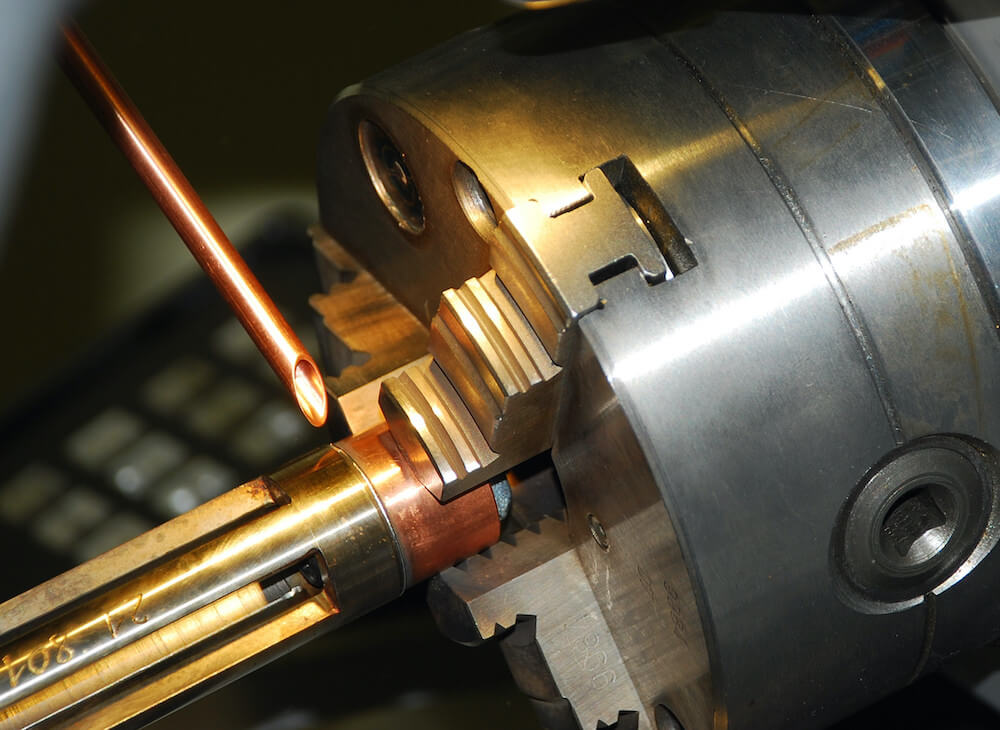
We offer laser welding in Ljubljana and Maribor, as well as in the field. We weld using modern lasers that enable high quality, precise and fast welding.
Our modern fibre lasers enable three types of welding: continuous, continuously modulated and pulsed. The devices offer a range of laser beam settings, one of which is the laser flash design, the shape of which can be configured in any way. This is particularly important when welding cracks, hard materials, polished materials, etc. The control devices are very flexible; the size and weight of the piece have never been a problem.
We guarantee the quality of laser welding with experienced welders and the highest quality welding wires. Some welders have been gaining experience since 2003. The quality of laser welding is checked in our accredited metallurgical laboratory. Beside the ISO 9001 system, we also have the ISO 17025 system in place.
We can also issue WPS, PQR or WPQR certification on request.
We also offer batch welding, as our lasers are also suitable for automation.
What is laser welding?
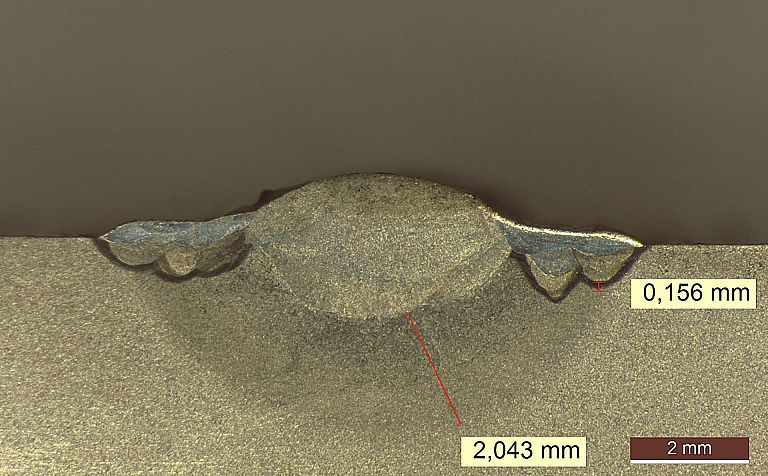
Laser welding is a high-precision welding process that uses a high-energy laser beam focused on a small spot. It can be welded with or without filler material. We use welding wires with diameters from 0.1mm to 0.8mm, though larger diameters can be used.
Benefits of laser welding: precision, miniaturisation, low heat input and consequently low deformation, the weld has virtually no peripheral indentation, the surroundings of the weld are intact, the weld is pleasing to the eye, etc. However, laser welding is slower in terms of the amount of material melted and more expensive than arc welding processes.
Examples of laser welding:
- the refurbishment welding of die-casting tools, forging tools, plastic and rubber injection moulding tools, etc.,
- welding of cutting tools, knives,
- welding of stainless products for the pharmaceutical, medical, food industry, etc.,
- welding of orthopaedic devices,
- welding of cryogenic products (helium leak test),
- welding parts for the aeronautic industry,
- filter welding,
- welding engine parts such as shafts (crankshaft, camshaft),
- welding non-ferrous metals (aluminium, copper, bronze),
- jewellery welding,
- welding various housings,
- welding exotic materials (titanium, gadolinium, nitinol, etc.),
- welding spiracles, etc.